BECE 2007 Integrated Science Objective Questions and Answers
Answer all questions in this section.
Each question is followed by four options lettered A to D. Find the correct answer for each question.
1. Which of the following properties is true about all matter? Matter has
Solution: All matter occupies space (volume) and has mass, but not all matter has a fixed shape (e.g., gases) or fixed density.
2. The type of energy obtained when an electric bulb is connected to a battery is
Solution: The bulb converts electrical energy from the battery into visible light energy, which is the primary output obtained.
3. A magnet can attract all these substances except
Solution: Magnets only attract ferromagnetic materials (e.g., iron, steel). Glass is non-magnetic and unaffected.
4. The process by which heat travels along a metal is called
Solution: Conduction involves direct transfer of heat through molecular collisions in solids, especially efficient in metals.
5. The instrument used to measure temperature is the
Solution: Thermometers specifically measure temperature via thermal expansion of liquids (e.g., mercury) or electronic sensors.
6. A stick placed in water appears to be bent because light travelling from the water to the air is
Solution: Refraction bends light rays at the water-air interface due to the change in light speed, causing visual distortion.
7. A plane mirror could be described as opaque because it
Solution: Opaque materials do not transmit light; mirrors reflect nearly all incident light, making them functionally opaque.
8. A suitable machine for loading drums of palm oil onto a truck is
Solution: An inclined plane reduces effort by allowing gradual elevation change, ideal for rolling heavy drums upward.
9. The human forearm is an example of
Solution: The elbow acts as the fulcrum, effort is applied by biceps near the fulcrum, and resistance (e.g., weight) is at the hand—a third-class lever.
10. The chemical substances which help in the digestion of food are known as
Solution: Enzymes catalyze the breakdown of complex food molecules (e.g., amylase for starch) during digestion.
11. Digestion of proteins starts from the
Solution: Pepsin in gastric juice begins protein hydrolysis in the acidic environment of the stomach.
12. A reflex action involves the
Solution: Reflex arcs bypass the brain; sensory neurons relay signals to the spinal cord, which directly triggers motor neurons.
13. Which of the following structures is not part of the central nervous system?
Solution: Veins are blood vessels unrelated to the CNS, which comprises the brain and spinal cord only (nerves are peripheral).
14. When the testa of a soaked bean is removed, the seed is seen to be made up of
Solution: Cotyledons (seed leaves) form the bulk of the seed, storing nutrients and becoming visible after testa removal.
15. One function of the root system of plants is to
Solution: Roots anchor plants via branching and root hairs, preventing displacement while absorbing water/minerals.
16. Which of the following diseases is caused by a virus?
Solution: CSM is caused by viral (e.g., enteroviruses) or bacterial agents, but viral meningitis is common (cholera, TB, and malaria are bacterial/protozoan).
17. The different types of teeth that an animal has gives an indication of the nature of its
Solution: Teeth morphology (e.g., carnassials in carnivores, molars in herbivores) directly correlates with diet/feeding habits.
18. Exchange of gases takes place in the respiratory system through the
Solution: Gas exchange (O₂/CO₂) occurs in alveoli within the lungs, facilitated by capillaries and thin membranes.
19. Water that requires more soap in order to form lather is described as
Solution: Hard water contains Ca²⁺/Mg²⁺ ions that react with soap to form scum, reducing lathering efficiency.
20. One best way of making water safe for drinking is by
Solution: Boiling kills pathogens (bacteria, viruses) effectively, unlike filtering (which may miss microbes) or chemical additives.
21. The process whereby a hot saturated solution is cooled to obtain the solute is called
Solution: Crystallization uses cooling to reduce solute solubility, forming pure solid crystals from a saturated solution.
22. If a mixture of water and powdered charcoal is allowed to stand for a long time, the charcoal
Solution: Charcoal is insoluble and denser than water, leading to sedimentation due to gravity over time.
23. The chemical symbol of potassium is
Solution: Potassium's symbol is K (from Latin "kalium"), while Na is sodium, Pb is lead, and S is sulfur.
24. The atom of an element is represented as \( \frac{35}{17} \)Cl. How many electrons are in the atom?
Solution: The atomic number (17) equals proton count; in a neutral atom, electrons equal protons (17).
25. Which of the following agricultural practices prevents loss of water from the soil?
Solution: Mulch (e.g., straw) reduces evaporation by shading soil and blocking wind exposure.
26. Soil conservation is important because it prevents loss of
Solution: Erosion washes away mineral nutrients (N, P, K), degrading soil fertility for agriculture.
27. Foot rot disease in animals is caused by
Solution: Fungal pathogens (e.g., Fusarium spp.) invade hooves/tissue, causing rot in livestock.
28. A patient with symptoms of diarrhoea and vomiting may be suffering from
Solution: Cholera (Vibrio cholerae) causes severe watery diarrhea/vomiting; dysentery involves blood, influenza is respiratory.
29. Which of the following human activities pollutes the environment?
I. Release of cement dust into the atmosphere
II. Dumping of refuse into water bodies
III. Burning of rubbish
Solution: Cement dust (air pollution), refuse dumping (water pollution), and burning rubbish (air/soil pollution) all harm the environment.
30. Which of the following features of a parent would not be inherited by the children?
Solution: Scars are acquired physical traits, not encoded in DNA; eye color, nose shape, and height involve genetic inheritance.
31. Which of the following bodies is at the centre of the solar system?
Solution: The Sun contains 99.8% of the solar system's mass, with planets orbiting it gravitationally.
32. The chemicals used in the preparation of ammonia in the laboratory are
Solution: Heating NH₄Cl with Ca(OH)₂ produces ammonia gas: 2NH₄Cl + Ca(OH)₂ → CaCl₂ + 2NH₃ + 2H₂O.
33. Steel is an alloy of
Solution: Steel primarily combines iron with 0.1–2% carbon; brass is copper-zinc, and iron-zinc is galvanized coating.
34. The property of a metal that makes it possible for it to be beaten into different shapes is called
Solution: Malleability allows metals to deform under compression (e.g., hammering) without breaking.
35. Movement of the particles of a gas from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration is known as
Solution: Diffusion describes spontaneous particle movement down a concentration gradient (e.g., perfume spreading in air).
36. Oxygen in the blood finally reaches the parts of the body through the
Solution: Capillaries are thin-walled vessels enabling O₂ diffusion from blood to tissues via their extensive network.
37. An aluminium cube with side measuring 2 m has a mass of 24 kg. Calculate the density of the aluminium.
Solution: Density = mass/volume. Volume = 2m × 2m × 2m = 8 m³. Density = 24 kg / 8 m³ = 3 kg/m³.
38. The force that opposes the motion of an object on another object is called
Solution: Friction acts parallel to surfaces in contact, resisting relative motion (e.g., sliding, rolling).
39. Water is prevented from passing through the tiny holes in an umbrella by
Solution: Surface tension creates a cohesive "skin" on water, resisting penetration through small openings.
40. Which of the following methods of preserving food makes use of heat energy from the sun?
Solution: Sun-drying evaporates moisture using solar heat, inhibiting microbial growth in foods like grains/fruits.
1. Question 1
1.(a) In an experiment, an iron bar is magnetized by dragging a magnet over the surface of the bar from end A to end B several times as shown in the diagram below.
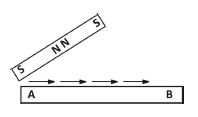
(i) Mention the method of magnetization
(ii) Give the polarity of the ends A and B of the bar after the magnetization.
(iii) How will you test that the bar AB is a magnet?
(iv) Indicate how you will test for the poles of A and B of the bar
(v) Give one precaution that should be taken during the magnetization process.
(vi) Name one other method of magnetization
(b) The set-up below is used to prepare gases in the laboratory
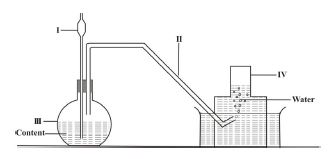
(i) Give the names of the parts labelled I, II, III and IV
(ii) Write down the two names of the method of gas collection
(iii) Explain how the gas collects over the water
(iv) Name two gases that can be prepared using the set-up
(c) The set-up below shows air being breathed out through the mouth into test-tube containing lime water
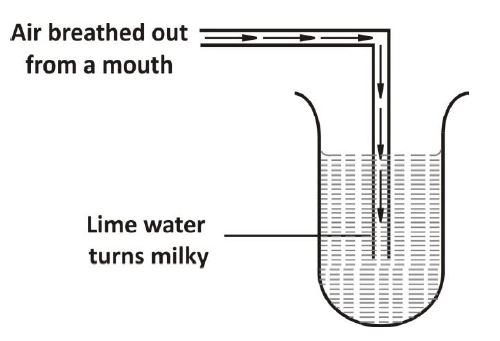
(i) Why does the lime water turn milky?
(ii) Identify the milky substance produced.
(iii) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
(iv) Name two other substances present in breathed-out air.
(v) What is the aim of the experiment?
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 1
1.(a) (i) Single Stroking or single stroke
(ii) A: South pole; B: North pole
(iii) - Bring the bar close to iron material (e.g., nails, pins, clips); materials get attached.
- Hold near a plotting compass; compass deflects.
- Suspend horizontally with string; comes to rest in North-South direction.
- Bring a magnet close to one end; attraction/repulsion occurs.
(iv) - Bring south pole of known magnet near ends: repulsion at A (south), attraction at B (north).
- Bring north pole of known magnet near ends: attraction at A (south), repulsion at B (north).
(v) - Drag magnet in same direction always.
- Remove magnet completely from the bar after each stroke.
(vi) Electrical method / Hammering / Double stroke / Induction
1.(b) (i) I: Thistle funnel; II: Delivery tube; III: Flat-bottomed flask; IV: Gas jar
(ii) Upward delivery; Downward displacement of water
(iii) Gas molecules (lighter than water) rise, exert pressure on water, and force it downward.
(iv) Hydrogen / Carbon dioxide / Oxygen
1.(c) (i) Presence of carbon dioxide in exhaled air.
(ii) Calcium carbonate (or Calcium trioxocarbonate(IV) / CaCO₃)
(iii) Ca(OH)₂ + CO₂ → CaCO₃ + H₂O
(iv) Nitrogen, water vapour, inert gases, unused oxygen
(v) To show carbon dioxide is present in exhaled air / a by-product of respiration.
2. Question 2
2. (a) What is a living cell?
(b) Give one function of each of the following components of a living cell:
(i) cell membrane
(ii) chloroplast
(iii) nucleus
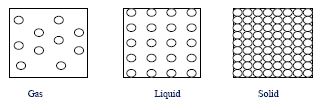
(c) Make sketches to show the arrangement of the particles in each of the three states of matter.
(d) What instrument would you use to measure each of the following quantities:
(i) volume of a liquid
(ii) mass of a stone
(iii) time
(iv) speed of the wind?
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 2
2.(a)
- Smallest independently functioning unit in a living organism.
- Most basic unit of a living organism that can function independently.
2.(b) (i) - Protects cell from chemical/physical changes.
- Regulates molecule movement into/out of cell.
(ii) - Contains chlorophyll/pigments.
- Site of photosynthesis.
(iii) - Carries genetic information.
- Directs most cell activities.
2.(c)
- Gas: Particles widely spaced, random motion.
- Liquid: Particles closer, irregular arrangement.
- Solid: Particles tightly packed, fixed positions.
2.(d) (i) Measuring cylinder / Burette / Volumetric flask
(ii) Top pan balance / Beam balance
(iii) Stop clock / Clock / Watch
(iv) Anemometer
3. Question 3
3. (a) Name three deficiency diseases associated with diet and state their causes.
(b) (i) What is hard water?
(ii) Mention three ways by which hard water can be made soft.
(c) (i) Explain how sound is produced.
(ii) State one example each of:
(a) wind instrument
(b) string instrument
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 3
3.(a) - Beriberi (Lack of vitamin B₁)
- Kwashiorkor (Lack of protein)
- Rickets (Lack of vitamin D)
- Scurvy (Lack of vitamin C)
- Night blindness (Lack of vitamin A)
- Goitre (Lack of iodine)
3.(b) (i) Water that does not lather easily with soap.
(ii) Boiling / Adding washing soda / Distillation
3.(c) (i) Sound is produced when a vibrating body causes air particles to vibrate.
(ii) (a) Flute / Trumpet / Horn / Clarinet
(b) Guitar / Harp / Violin / Cello / Piano
4. Question 4
4. (a) State two examples of:
(i) carnivore
(ii) herbivore
(b) What is the difference between egestion and excretion?
(c) Explain briefly why:
(i) gold is used to make necklaces and earrings.
(ii) steel is used instead of iron to make car bodies.
(d) (i) What is surface tension?
(ii) Explain why the surface of water in a container is curved.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 4
4.(a) (i) Lion / Tiger / Crocodile / Wolf / Hyena
(ii) Goat / Cow / Grasshopper / Sheep / Grasscutter
4.(b) - Egestion: Removal of undigested food.
- Excretion: Removal of metabolic waste.
4.(c) (i) - Highly non-reactive (resists staining).
- Malleable (easy to mold).
- Lustrous (attractive appearance).
(ii) - Steel (iron + carbon) is stronger and rust-resistant; iron rusts easily.
4.(d) (i) Property making liquid surfaces behave like stretched elastic skin.
(ii) Adhesive forces (water-container) > cohesive forces (water-water), causing upward curvature.
5. Question 5
5. (a) Copy and complete the table:
| Disease | Causative Agent | Prevention/Control |
|---|---|---|
| Cholera | Vibrio spp. | Eating hot food |
| (i) ……….. | Plasmodium | (ii) ……….. |
| (iii) ……….. | Louse | Personal hygiene |
| Ringworm | (iv) ……….. | (v) ……….. |
(b) Name two particles of matter which carry
(i) negative charge
(ii) positive charge
(iii) no charge
(c) A machine moves a 20N load 2m using 25N effort moving 4m. Calculate:
(i) work input
(ii) work output
(iii) efficiency
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 5
5.(a)
| Disease | Causative Agent | Prevention/Control |
|---|---|---|
| Cholera | Vibrio spp. | Eating hot food |
| Malaria | Plasmodium | Mosquito nets/repellents; anti-malaria drugs; clearing stagnant water |
| Relapsing fever / Typhus | Louse | Personal hygiene |
| Ringworm | Fungus | Keep skin dry; avoid contact; antifungal medication |
5.(b) (i) Electron / Negatron / Anion
(ii) Proton / Positron / Alpha particle / Cation
(iii) Neutron / Atom / Molecule
5.(c) (i) Work input = 25N × 4m = 100 J
(ii) Work output = 20N × 2m = 40 J
(iii) Efficiency = (40 J ÷ 100 J) × 100% = 40%